Introduction to C++
C++ is a powerful and versatile programming language that is used to develop a wide range of applications, from system software to games to web applications. It is an extension of the C programming language and provides additional features such as object-oriented programming, templates, and exception handling.
Some of the IDEs that you can use for C++ programming are:
- CodeBlocks with the MinGW compiler.
- Visual Studio Code with the C++ extension.
- Cxxdroid for Android devices.
- cppCode for iOS devices.
- OnlineGDB an online IDE for C++. However, I would still recommend installing an IDE on your device so that you can code offline.
Although, I highly recommend programming on a computer rather than a mobile device, as it is easier to code and debug on a computer, and there are some features that are not available on mobile devices.
How to Start Programming in C++
Here’s how you can start programming in C++ with some of the IDEs mentioned above:
CodeBlocks
-
Open CodeBlocks. You can either find the shortcut on your desktop or search for it in the Start menu.
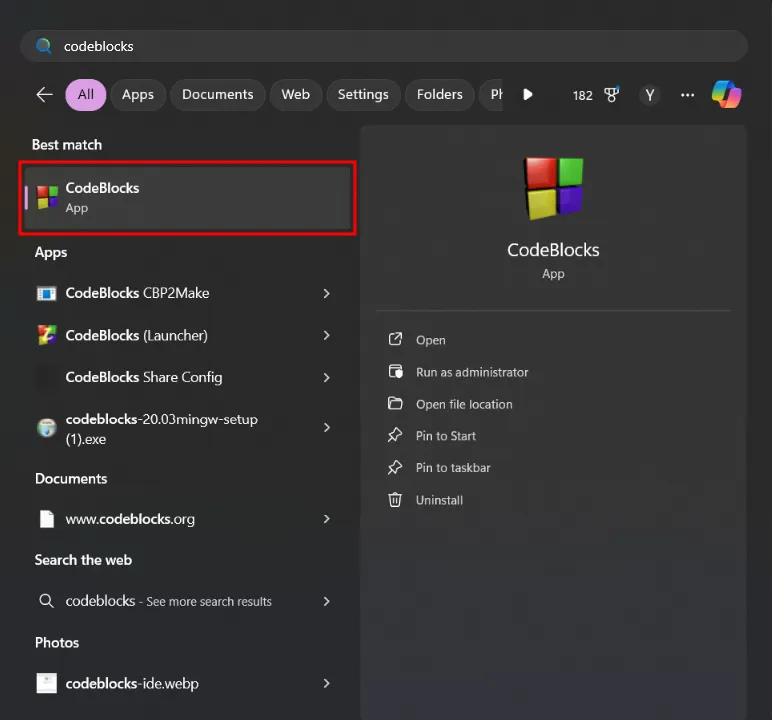
-
Create a new project.
Click on the File menu and select
New>Project....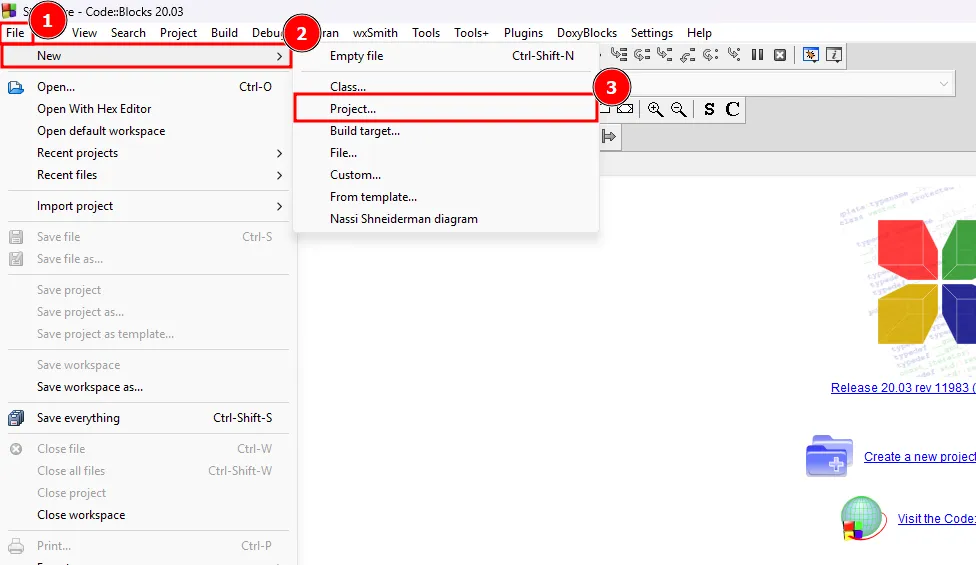
-
Select the correct template.
Double click the
Console ApplicationProject Template.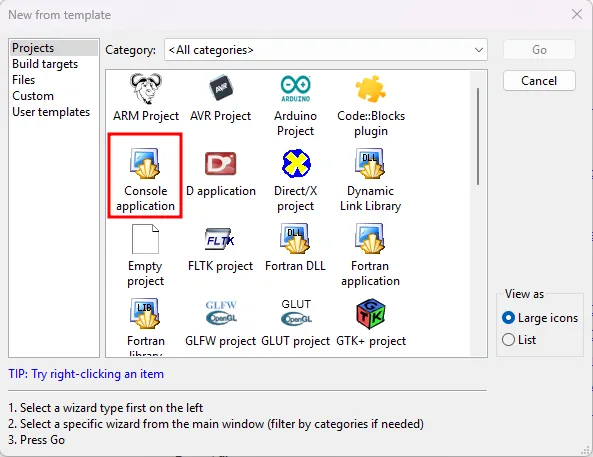
-
Select the language type and project details.
Select
C++as the language and clickGo, then set the project title and location. The other fields gets filled automatically, so leave it as is.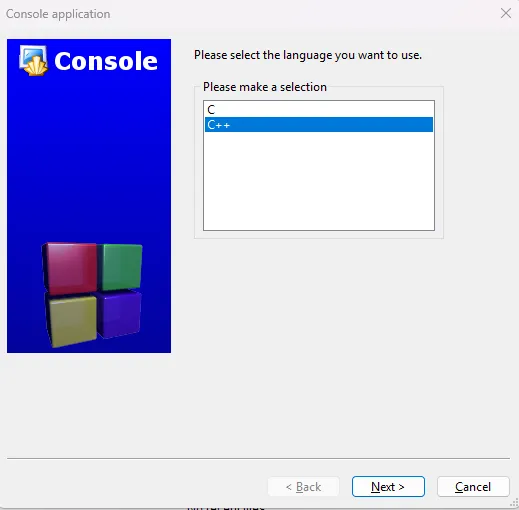
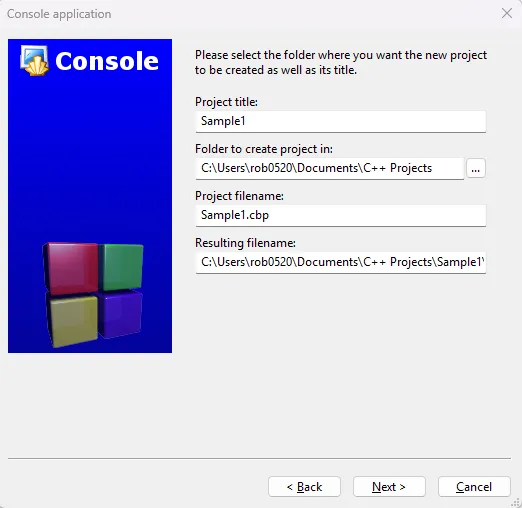
-
Select the Compiler.
Afterwards, set the Compiler as
GNU GCC Compilerand clickFinish.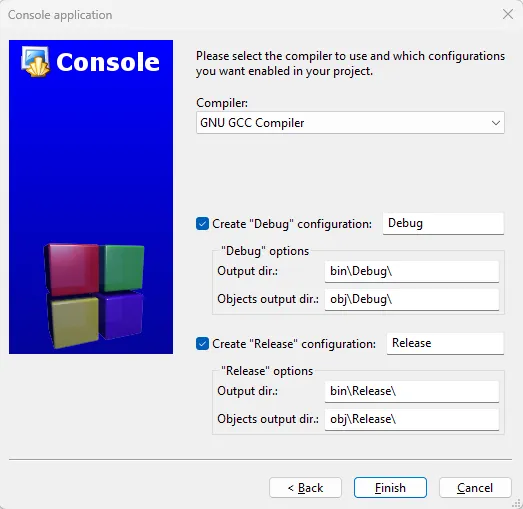
Important Parts of Codeblocks
There are a lot of buttons and menus in CodeBlocks, but here are some of the important ones that you will use often:
- Compiler Buttons: There are three buttons that you will often use as you code in C++. From left to right, They are the
Build,Run, andBuild and Runbuttons.
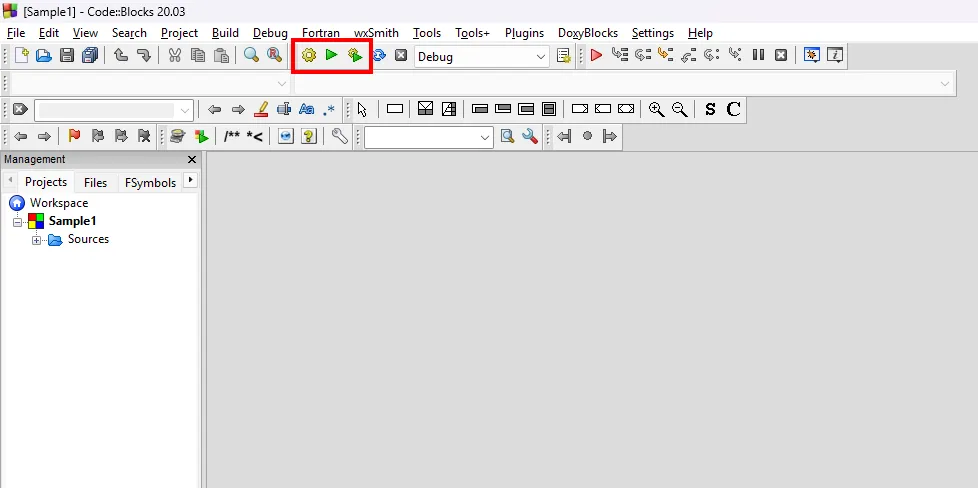
When you click the Build button, CodeBlocks will compile your code and check for any errors. If there are no errors, it should open a Terminal window with the output of your program.
If you click the Run button, CodeBlocks will run the last compiled program.
And if you click the Build and Run button, CodeBlocks will compile your code and run the program afterwards. This is the button that you will often use when you are coding, instead of needing to click the Build button and then the Run button separately.
- Management Area: Under the Project Tab in the Management Area, you can see the files that are in your project. Including the
main.cppfile, which is the file that you will be coding in, found under the Sources folder.
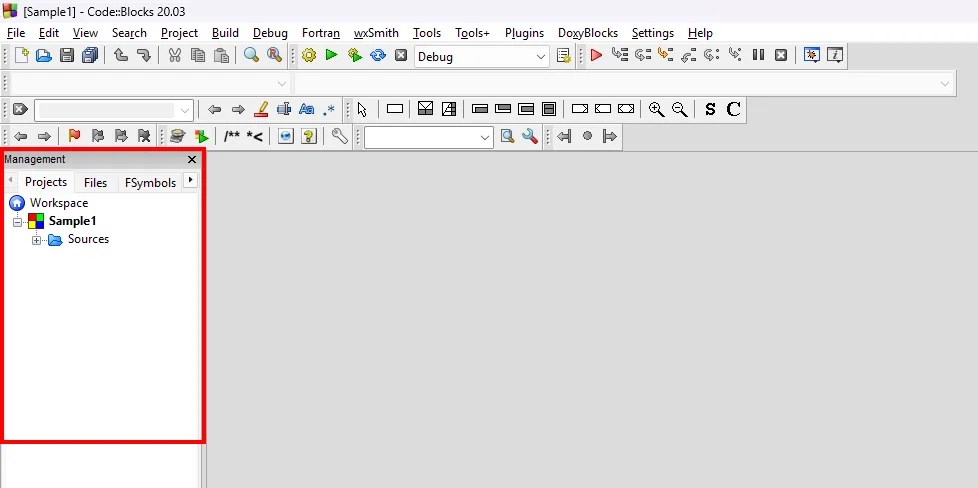
Incase you cannot see the Management Area, you can click on the View menu and select Manager to show it.
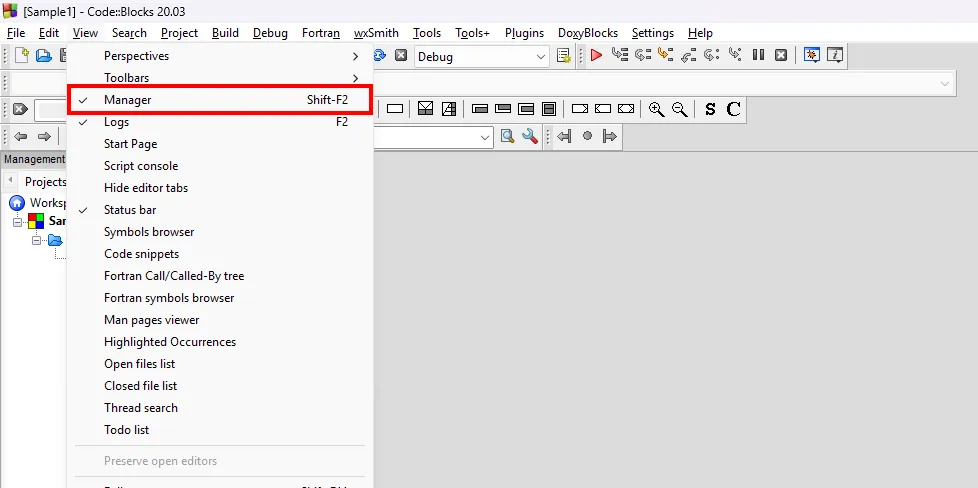
- Logs Window: In this window there are several kinds of logs. The most important one is the
Build logwhich shows the output of the compiler when you click theBuildor theBuild and Runbutton.
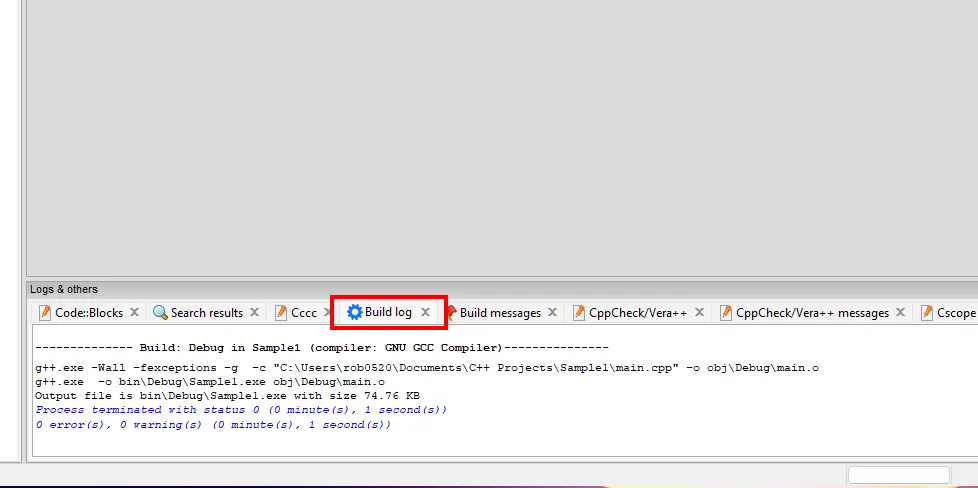
If you cannot see the Logs Window, you can click on the View menu and select Logs to show it.
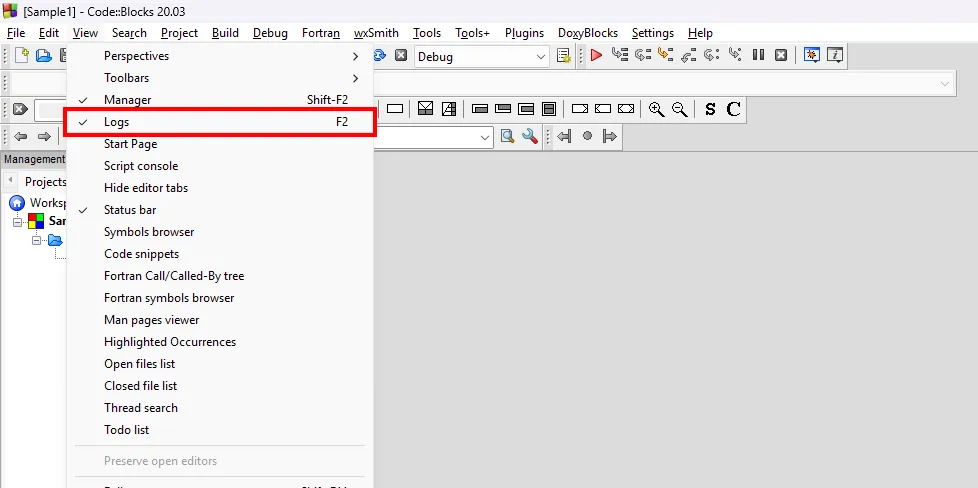
Cxxdroid
-
Open Cxxdroid.
You can either find the shortcut on your home screen, search for it in the app drawer or open it in the Play Store.
-
You’re good to go, you can start coding in C++ right away.

-
To run your code, you can click the
Runbutton at the bottom-right corner of the screen.
Main Structure of a C++ Program
Here is the basic structure of a C++ program:
Library Declarations
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() { // Your code here return 0;}The number sign or hash # is used to include libraries in C++. The iostream library is used for input and output operations in C++.
Namespace Declaration
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() { // Your code here return 0;}The using namespace std; statement tells the compiler to use the std namespace. The std namespace contains the standard C++ library. This means that you can use the functions and objects in the std namespace without having to write std:: before each function or object. For example, you can write cout instead of std::cout.
Main Function
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() { // Your code here return 0;}The main() function is the entry point of a C++ program. The program starts executing from the main() function. The int before the main() function indicates that the function returns an integer value. The return 0; statement at the end of the main() function indicates that the program has executed successfully.