Introduction to HTML
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the standard markup language for creating web pages. It describes the structure of web pages using markup. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages, and are represented by tags. HTML tags label pieces of content such as “heading”, “paragraph”, “table”, and so on.
HTML is written in the form of HTML elements consisting of tags enclosed in angle brackets (like <html>), within the web page content. HTML tags most commonly come in pairs like <h1> and </h1>, although some tags, known as empty elements, are unpaired, for example <img>.
Running HTML Code
You can run HTML code in your browser by creating an HTML file and opening it in your browser. However, here’s how I recommend you run HTML code with VSCode and the Live Server extension:
-
Prepare your files
Prepare all the files you need for your website, including the HTML, and CSS files.
-
Run Live Server
Right-click on the main HTML file(in this case the
index.htmlfile) and selectOpen with Live Server.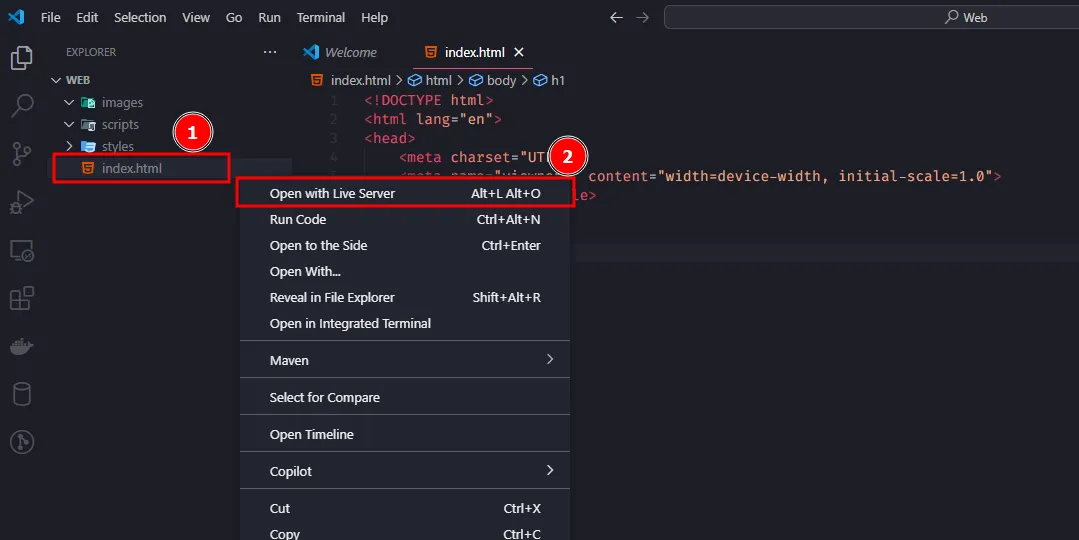
-
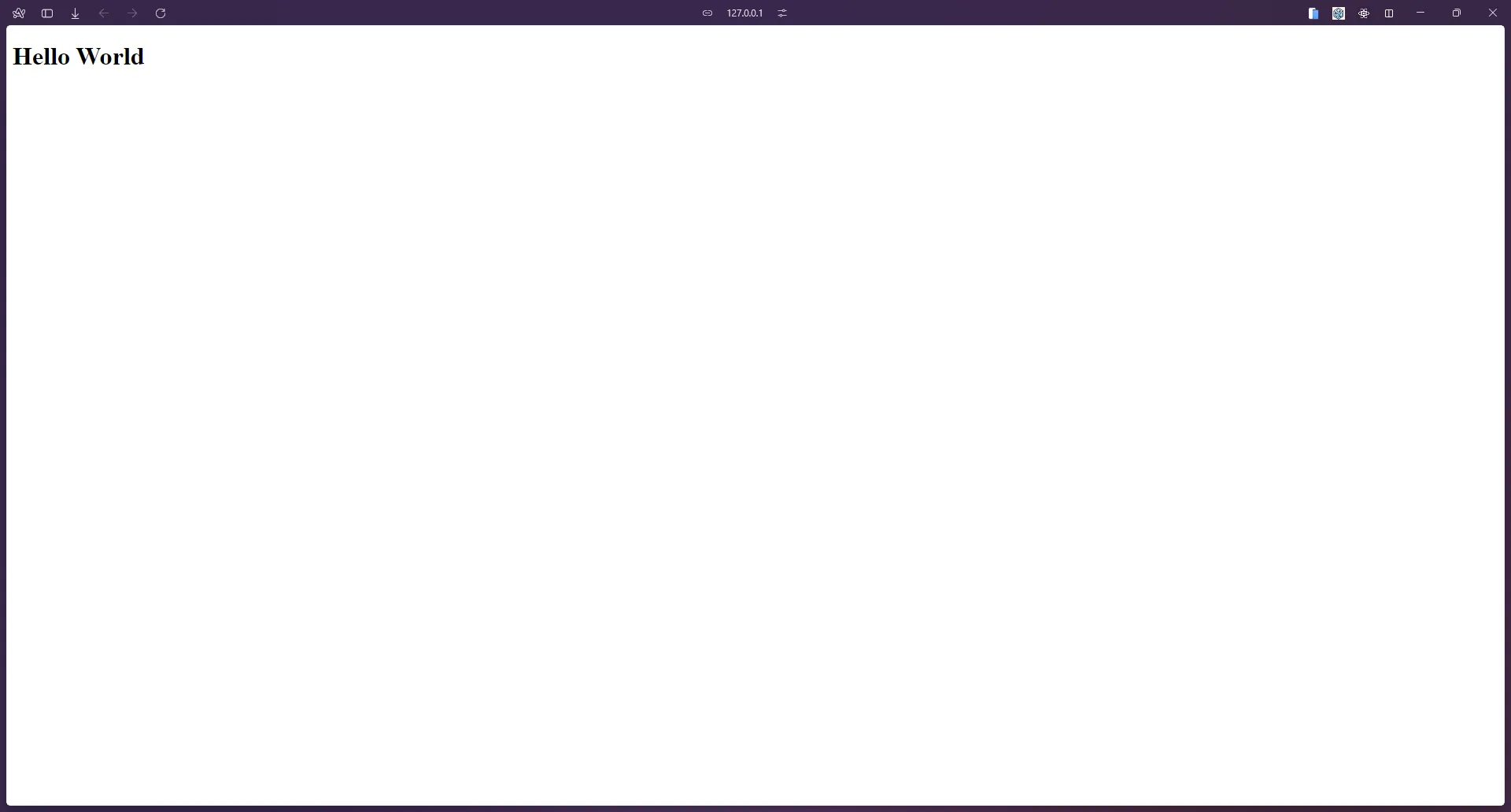
View your website
Your website should open in your default browser. You can now see your website live and make changes to the code.
HTML Structure
Typically, this is how an HTML document looks like:
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Page Title</title></head><body> <!-- Content goes here --></body></html>Here’s what each part of the document does:
Document Type Declaration
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Page Title</title></head><body> <!-- Content goes here --></body></html>The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration defines the document type and helps the browser to render the page correctly. It is important to include this declaration at the beginning of the HTML document, as it tells the browser that the document is an HTML5 document.
If you want you can also use HTML 4 or XHTML, but HTML5 is the latest version of HTML and is widely used. You can see what elements are available in each document type here.
<html> Element
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Page Title</title></head><body> <!-- Content goes here --></body></html>The <html> element is the root element of an HTML page. It is the container for all other HTML elements (except for the <!DOCTYPE html> declaration).
<head> Element
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Page Title</title></head><body> <!-- Content goes here --></body></html>The <head> element contains meta-information about the HTML document, such as the title of the document, links to stylesheets, scripts, and other meta-information.
<title> Element
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Page Title</title></head><body> <!-- Content goes here --></body></html>The <title> element specifies the title of the HTML document (which is shown in the browser’s title bar or tab).
<body> Element
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <title>Page Title</title></head><body> <!-- Content goes here --></body></html>The <body> element contains the visible page content. This is where you put all the text, images, videos, and other content that you want to display on the web page.
HTML Tags
HTML tags are used to define the structure of an HTML document. Here are some common HTML tags:
<h1>to<h6>: Headings<p>: Paragraph<a>: Anchor (link)<img>: Image<ul>: Unordered list<ol>: Ordered list<li>: List item<table>: Table
We will cover more HTML tags in the following sections. For now, you can refer to the MDN’s HTML Reference for a complete list of HTML tags.
Recommended HTML Structure
Here is how I recommend you structure your HTML document:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title></head><body> <!-- Content goes here --></body></html>The <meta charset="UTF-8"> tag specifies the character encoding for the HTML document. The <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> tag sets the viewport width to the device width and sets the initial zoom level to 1.0. This is important for responsive web design. The lang="en" attribute in the <html> tag specifies the language of the document. You can change en to the language code of your choice.